- What is the best ice gel pack for sports injuries recovery?
- Video: How to use hot and cold gel packs?
- Types of hot & cold packs you should know about
- What are the most common sports injuries that we can treat with hot and cold therapy?
- How to treat sports injuries with heat and cold therapy?
- How to use hot & cold gel packs to reduce inflammation in sports injuries?
- The best hot and cold gel packs for pain relief
The use of hot and cold gel packs to heal inflammation in all types of sports injuries can be extremely effective. Especially for various conditions and muscle injuries caused by intense physical activity that cause stiffness, pain and swelling.
But first, let's talk about the most common sports injuries and how to properly treat them with cold, heat and hot & cold therapy.
What is the best ice gel pack for sports injuries recovery?
- Size: One size fits all
- Colours: Grey and Black
- Material: Breathable
- No. of products: 1 Piece
- Uses: Rehabilitation and sport
- Always Flexible
- High Quality
- Full Pack
- Extra-Strong Velcro
- Ergonomic design

Extra-Strong Velcro

High Quality

Always Flexible
Euphoria Bliss - Hot and Cold Reusable and Flexible Gel Ice Pack for Pain Relief with velcro Straps
- Material: Nylon
- Uses: Back, Shoulders, Neck, Waist and Legs
- Type of adjustment: Velcro strap
- Cover: No
- No. of units: 1
- Various models
- Fully adjustable
- Heat/cold therapy
- Suitable for pets
- Short therapy duration
- Bulky design
The adjustable strap will provide stability and compression to the joint, so the pain will also be reduced by the pressure therapy. It can be used during physical training or after a long day's work, as the feeling of fatigue and cramps disappear immediately. It can be used by anyone because its size adapts well to the anatomy of the leg, but consider that the fabric can cause irritations.
- Material: Nylon
- Uses: Knee, Ankle, Hip and Back
- Type of adjustment: Velcro strap
- Cover: Yes
- No. of units: 1
- Adjustable strap
- Protective cover
- Hot/cold therapy
- Quality materials
- Only one per order
- Only one size
You can also combine it with compression therapy because its elastic strap is anatomically adjustable to any body shape. This gives more stability and aligns the joint to generate greater support. You can use it on the ankle, calf and sole of the foot, which makes this thermal pillow a versatile health product. In some cases, the compression may be uncomfortable during use.
- Optimal fit
- Protective cover
- Heat/cold therapy
- Quality finish
- Bulky design
- Short cold/warm duration
Get the medical temperature by simply placing the heating pad in the freezer for two to three hours, helping you get the therapeutic benefits without breaking the bank. Use this versatile product when training or whenever you want to relax at home, as its materials will prevent slipping down your leg. Please note that in some cases, the double stitching will give way and the internal fluid will leak out.
- Velcro strap
- Optimal fit
- Hot/cold therapy
- Quality finish
- Only one per order
- Only one size
Prolonged use relieves symptoms of meniscus and ligament tears, inflammation in the patellar tendon and muscle tears. You only need to adjust the triple velcro strap and heat in the microwave or cool in the refrigerator the thermal pillows to support the sensitive areas. It can be used for fitness training or when you're at home, but be aware that compression may be ineffective in some cases.
- 3 Gel Packs
- Adjustable compression with quality finish
- One size fits all
This kneecap support has 4 adjustable straps strategically placed to immobilise harmful movements, which will also prevent muscle tears. You only have to remove the heating pads and place them on the inside, after getting the necessary temperature in the microwave or refrigerator. It is important to know that, in some cases, the heat does not last long and causes some discomfort.
- Material: Nylon
- Uses: Knee, Back and Neck
- Type of adjustment: Velcro strap
- Cover: Yes
- No. of units: 1
- Adjustable strap
- Suitable for various body areas
- Quality materials
- Adjustable compression
- Cold therapy only
- One size only
The cold therapy can be applied easily, you only need to place the band in the refrigerator for about 3 hours until the necessary temperature is reached to oxygenate the muscle and tendon fibres. You also have the option of applying the thermotherapy in just one minute in the microwave. The padding is reusable and can last for a long time, but be aware that further heating can cause burns and skin irritation.
Gelpacks Direct - Ankle Ice Pack Wrap for Sports Injuries, Plantar Fasciitis and Achilles Tendonitis
- Microwave safe
- Protective cover
- Heat/cold therapy
- Fully adjustable
- Smaller size
- One size only
To apply the heat therapy, simply place the gel pack in the microwave for two minutes. If you want to use cryotherapy, freeze the heating pad in the refrigerator for at least two hours to achieve the necessary temperature. When you combine these alternative treatments you will be able to apply compression by means of the elastic strap and achieve better results. In some cases it may be uncomfortable to use the heating pad.
- Heat/cold therapy
- Optimal fit with adjustable pressure
- Not suitable for microwave
For faster effects, complement the cold therapy with thermotherapy by simply heating the thermal pillow in the microwave or cooling it in the fridge. Sprains, swollen feet and Achilles tendonitis will be a thing of the past when you recover with the thermal support with gel packs. In some users the gel pack is not thick enough to maintain the temperature for a long time.
Video: How to use hot and cold gel packs?
Types of hot & cold packs you should know about
What are the most common sports injuries that we can treat with hot and cold therapy?
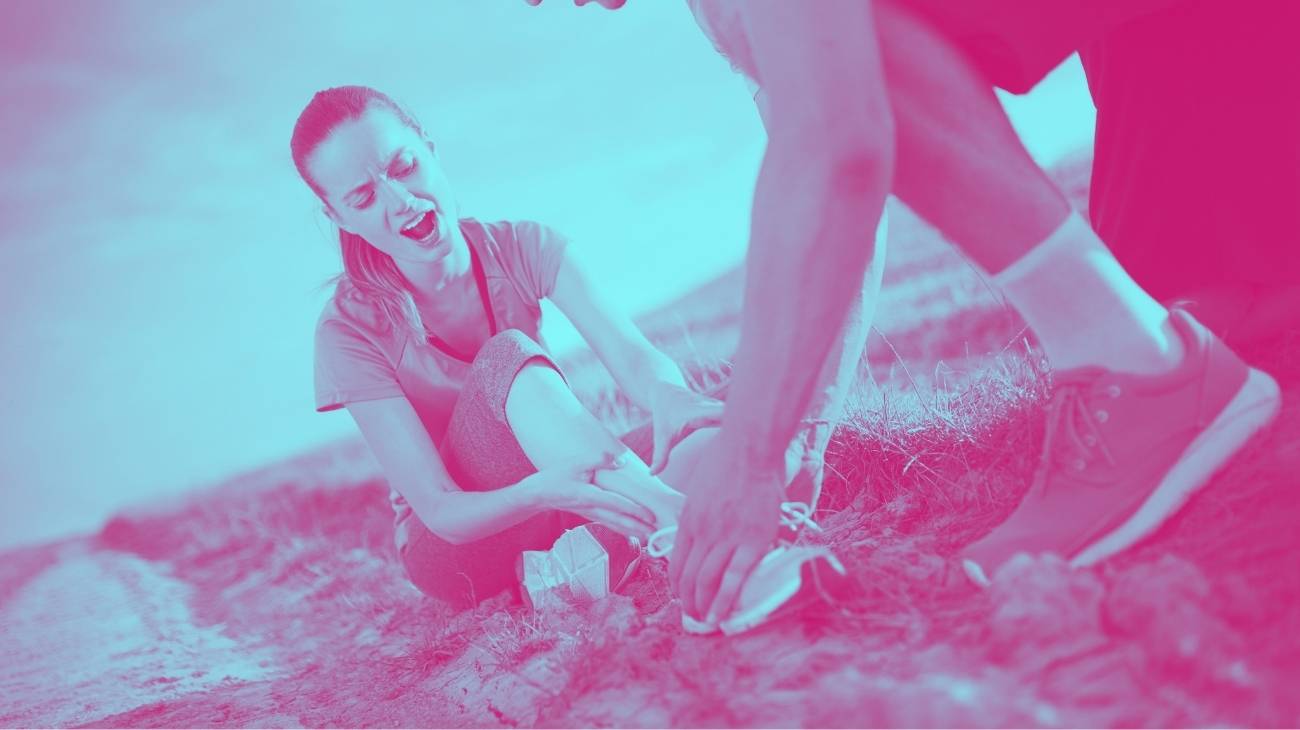
We know that sport is vital for our health because it keeps us active and healthy. Not only is it good for the heart, but it is also ideal for maintaining healthy breathing, maintaining and developing muscle strength and much more. However, one wrong move, a stumble, a fall or a blow can lead to sports injuries.
Therefore, we would like to inform you about the most common sports injuries so that you can recognise and prevent them:
Strains
It is caused by overuse of the muscle and tendons during sport or play. In muscles, all moving parts are susceptible to stretching or overuse, which can lead to tears, damage and pain. The most common include strains of the hamstring, tears of the quadriceps and groin strains. However, the best way to avoid them is to warm up and stretch before strenuous exercise.
Sprains
A sprain occurs when the ligament is incorrectly twisted, pulled and subsequently torn. The most common sprain among athletes and sportsmen is the ankle sprain, followed by knee, wrist and elbow sprains, to name a few. Good technique in your sport, warm-up exercises and stretching will help you avoid them.
Tendonitis
Tendonitis is inflammation of the tendon caused by excessive repetition of a particular movement. If not treated properly, tendonitis can lead to other injuries such as lateral epicondylitis, medial epicondylitis or patellar tendonitis.
Cruciate ligament tear
This is a tear of the anterior cruciate ligament (ACL). This is caused by sudden movements during a sudden stop, hard impact or change of direction as a tear occurs in this ligament. Symptoms of an ACL tear include a cracking or popping sound, severe pain and swelling.
Knee injuries
Athletic activity puts a lot of stress and wear and tear on the knee, leading to a variety of injuries. The most common include dislocations, fractures, muscle tears and tears of the anterior cruciate ligament. A knee injury can be very painful and disabling and may even require surgery. Again, good technique and posture when playing sports, combined with warm-up and stretching exercises, will help prevent them.
Fractures
Fractures or broken bones occur during strenuous or high-impact sports, especially in the legs, arms and feet. They are characterised by severe pain and immobility, and in some cases surgery is required to repair them. Playing should also be avoided when pain is present, as pain is a sign of a sprain or strain. If the bone is not treated properly, it is prone to fracture.
Tennis elbow
This is a very common injury in tennis players, golfers and other sports that place a lot of stress on the elbow. This strain is caused by repetitive movements over a long period of time. It is therefore recommended to warm up, stretch and take breaks before the day's play.
Sciatica
People who play golf, tennis, cycling, running or other sports that require insufficient stretching are likely to suffer from pain along the sciatic nerve. The course of this nerve runs from the lower back to the hips, buttocks and legs.
Plantar fasciitis
Plantar fasciitis is another common sports injury that occurs in football players, basketball players, runners and others. The high stresses of running, stopping, starting or dodging quickly lead to overactivity of the feet and legs. Combined with inadequate support, this leads to inflammation of the arch tendon, causing severe pain with each step.
How to treat sports injuries with heat and cold therapy?
Although we are all prone to injury, athletes are even more prone to injury. This is because their bodies are exposed to sudden, rapid movements due to intense physical activity. Cold, heat and contrast therapy play an important role in treating the pain and inflammation associated with these injuries. They have been shown to relieve pain, reduce inflammation and shorten recovery time.
We tell you here:
Cold therapy
Cold is ideal for treating pain from injuries caused by intense physical activity. It is a natural analgesic that numbs the injured area, slowing down pain signals to the brain. Cold therapy is also a very effective anti-inflammatory as it reduces blood flow to the injured area, thereby reducing swelling.
However, the effectiveness of cold is increased if it is applied early, before the first 48 hours after an acute injury. It is also indicated for chronic injuries, provided there is a flare-up, otherwise it would increase stiffness. Cold should also be used to treat tendonitis, back and neck pain. Cold should also be used for pain, limited joint mobility and to prevent delayed onset muscle soreness (DOMS).
Heat therapy
Heat has a very positive effect in treating sports injuries, especially those that cause muscle pain and discomfort. Heat therapy works by dilating blood vessels and increasing blood flow to the injured area, causing the muscles to relax. It is therefore highly recommended for the treatment of arthritis, joint stiffness, muscle strains and pulled muscles.
The use of heat is also indicated in the elimination of lactic acid waste produced during anaerobic exercise. This by-product accumulates in the muscles and causes pain. Heat therapy is also used to treat muscle spasms in the back. Not least because it has an analgesic and relaxing effect on tense muscles.
In the case of an acute injury, heat should be applied as soon as the swelling has gone down. But for athletes, heat is very effective before exercise as it increases flexibility and range of motion, preventing injury.
Hot and cold therapy
Doctors and physiotherapists recommend alternating heat and cold to control and relieve the pain of injuries. A freshly injured muscle should be treated with a combination of cold and heat. The cold helps to reduce swelling. Heat helps to reduce pain, aid healing and relieve muscle stiffness after the swelling has gone down.
After a sports injury, the alternation of heat and cold creates a "pumping" effect in the circulatory system. First, the blood flow in the injured area is restricted to reduce the swelling, and then the blood flow in that area is increased. This pumping effect is associated with mild aerobic activity and is therefore indicated for recovery from sports injuries that prevent movement.
This temperature contrast allows faster recovery from pain and improves range of motion. However, this type of therapy is recommended for injuries that last a week or more and for which the application of heat and cold alone has no effect. Similarly, hot & cold therapy is indicated for low back pain, and is used in combination with pharmacological treatment to relieve pain and discomfort.
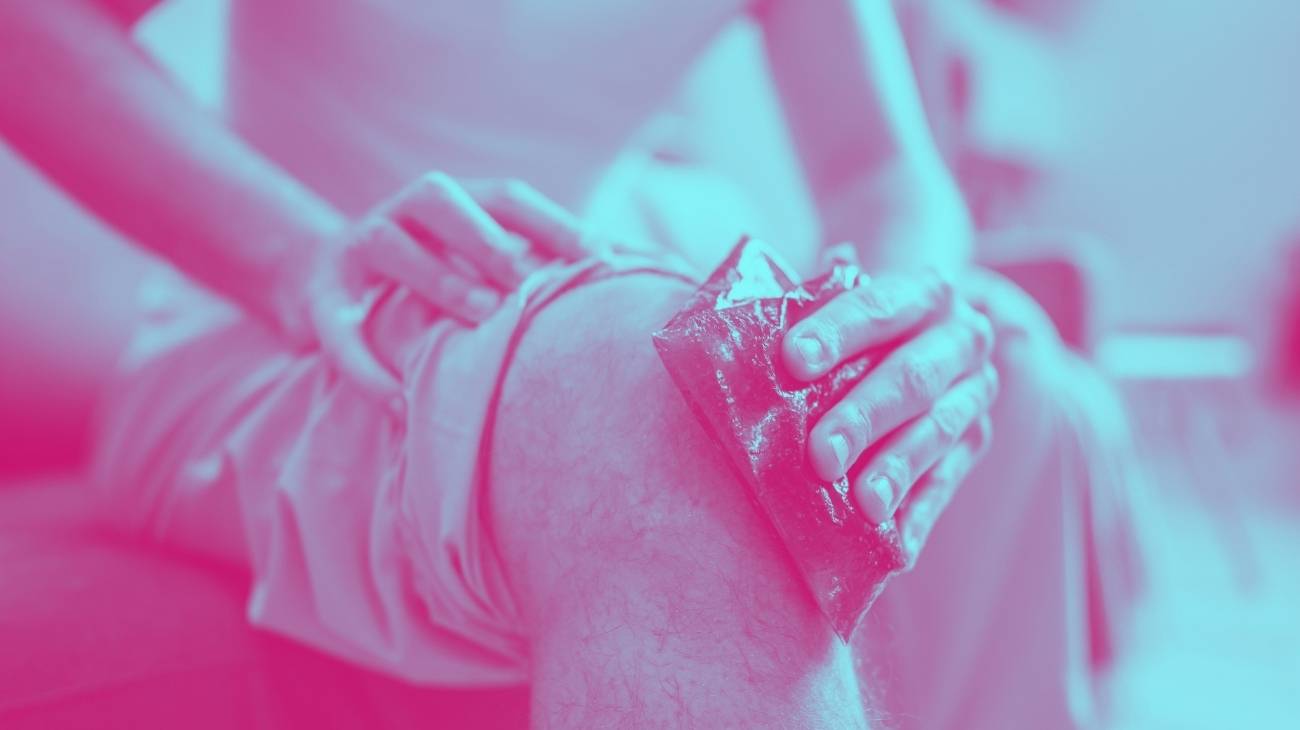
How to use hot & cold gel packs to reduce inflammation in sports injuries?
The use of heat or cold gel packs is indicated to reduce swelling in sports injuries, but do you know how to use them? If your answer is no, below is everything you need to know:
Using cold
For the safe use of cold gel packs for sports injuries, you should consider the following points:
- You should freeze the gel pack at least 2 hours before use for best results.
- Check that the temperature feels just right.
- Place the cold gel pack on the lesion. This process is very safe as our gel packs have a soft touch cover. However, for other commercial brands you should read the instructions as this depends on the manufacturer.
- The duration of cold exposure should not exceed 20 minutes.
- You can combine the cold with elevation of the affected area.
- After the treatment, the compress should be put back in the freezer.
- Repeat the cryotherapy sessions 2 or 3 times a day.
- You can do this for 3 days in a row.
- It is important to observe the injured area every 5 minutes while the compress is applied. Remove the product immediately if you notice any redness or discolouration.
- Do not use cold before exercising.
- Avoid cold therapy on poor circulation, diabetes, open wounds, sutures or infected wounds. Also, do not use it on people with limited sensitivity to cold, such as
Use hot
Depending on the type of sports injury, you should apply heat to relieve pain and promote healing. However, to ensure the effectiveness of heat therapy, the following recommendations should be followed:
- Cook the gel pack in the microwave for 30 seconds if the appliance's power setting is 800W. For other power settings, you will need to adjust the time before you reach the correct setting.
- Touch the hot gel pack to make sure it is at a tolerable temperature.
- Massage the gel with your hands to distribute the heat evenly.
- If it is not too hot, repeat the process for another 10 seconds in the microwave.
- To heat the gel pack on the cooker, boil about 3.5 litres of water. Then remove from the cooker.
- Soak the gel packs for up to 7 minutes.
- Remove and dry the gel pack with a blunt piece of wood.
- Make sure the gel pack is not overheated before placing it on the lesion.
- Do not heat the gel pack in the oven.
- Do not apply the gel pack after physical exertion, if the injured area is numb or if there is a burn or open wound. Do not apply the gel pack if you have a fever or heat stress.