- What is the best ice gel pack for sprain and strain?
- Video: How to use hot and cold gel packs?
- Types of hot & cold packs you should know about
- What are the causes of muscle sprain?
- What is better for relieving muscle pain from sprains or strains: cold or heat?
- How do you use hot & cold gel packs to relieve sprains and muscle strains?
- The best hot and cold gel packs for pain relief
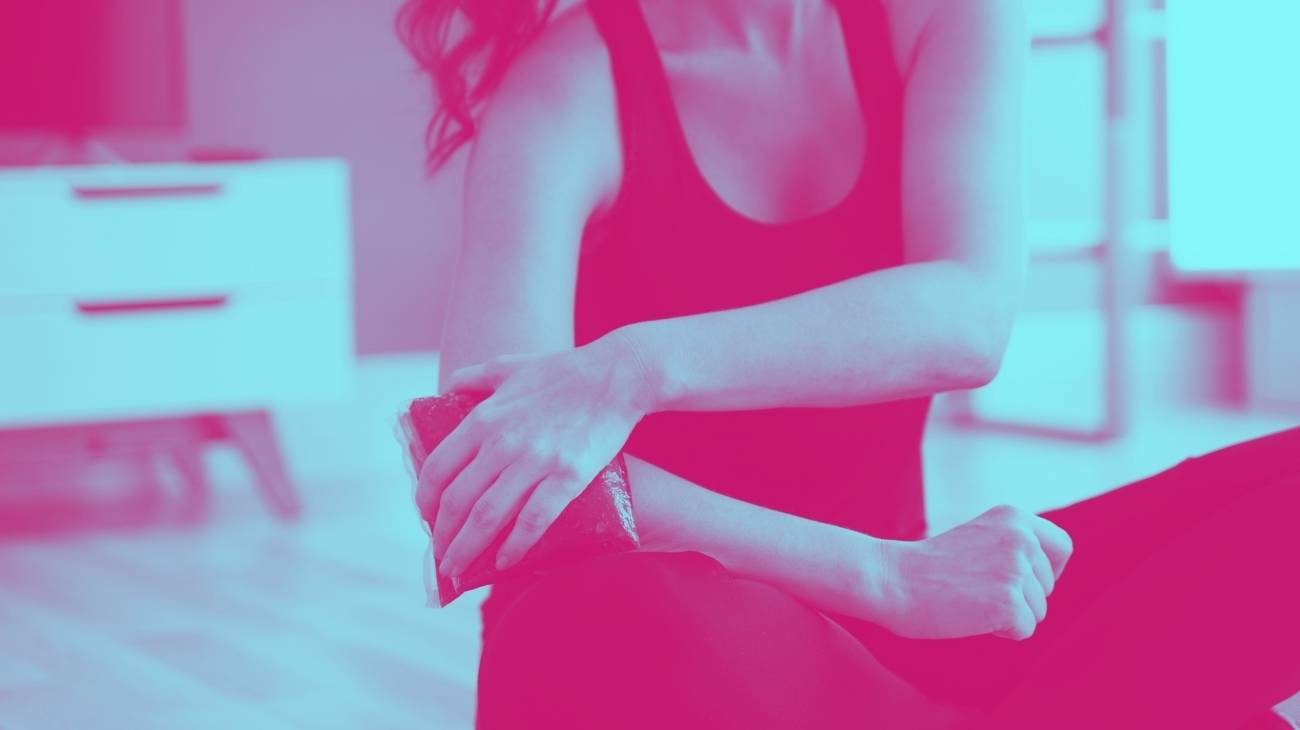
Sprains andpulled muscles are among the most common musculoskeletal injuries. Although they are usually very painful and uncomfortable, they are not very serious and dangerous injuries.
The use ofhot and cold gel packs to relieve sprains and muscle strains is often the easiest and most comfortable method. It is very effective when done correctly, and the best part is that it has no side effects. If you would like to know more about this therapy, come and see us.
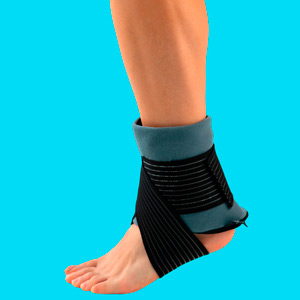
What is the best ice gel pack for sprain and strain?
- Size: One size
- Colors: Grey and Black
- Material: Breathable
- No. of products: 1 Piece
- Uses: Rehabilitation and sports
- Always Flexible
- High Quality
- Complete pack
- Extra-Strong Velcro
- Ergonomic design

Extra-Strong Velcro

High Quality

Always Flexible
- Material: Nylon
- Uses: Back, Ankle, Knee, Shoulder
- Adjustment Type: Velcro Strap
- Cover: Yes
- No. of units: 1 Gel Pack
- Hot/cold therapy
- Adjustable Velcro strap
- Microwaveable
- Good flexibility
- Short-lasting heat therapy
- Delicate wash
Arthritis, golfer's elbow syndrome and inflammation from trauma can be easily treated with this recovery support . Place in the refrigerator or freezer to get the temperature you're looking for and then place it on the side of your elbow to help you recover faster. Sweat buildup can be uncomfortable for some users and cause shifting during use.
- Hot/cold therapy
- Suitable for various body areas
- Low flexibility with cold therapy
It is suitable for use with the refrigerator or microwave, in case you want to apply heat therapy. Its materials keep the temperature controlled in sensitive areas to improve blood circulation and achieve faster natural healing effects. Keep in mind that gel pads may cause unpleasant odors during use.
- Material: Nylon
- Uses: Various body areas
- Type of adjustment: Velcro strap
- Cover: Yes
- No. of units: 2 Gel Packs
- Microwave safe
- Hot/cold therapy
- Quality materials
- Adjustable Velcro strap
- Medium flexibility with cold therapy
- Delicate wash
If you are looking to shorten recovery time from injury, you can use this adjustable thermal elbow pad on a daily basis by simply getting the pads to the required temperature by placing them in the microwave or refrigerator. Compression therapy can also be applied to the elbow with this versatile product, as its adjustable straps will help you find the ideal pressure to stimulate blood circulation. During use, they may cause discomfort by slipping on the arm.
- Material: Nylon
- Uses: Elbow, Wrist, Knee
- Type of adjustment: Strap with Velcro
- Cover: Yes
- No. of units: 2 Gel Packs
- Includes 2 Gel Packs
- Long lasting cold therapy
- Cold therapy only
You will not need much time to achieve the therapeutic temperature, since by simply placing it in the microwave or in the refrigerator you will obtain the results you are looking for to apply to the affected area. Keep in mind that, during use, the adjustable straps may weaken and lose their holding capacity.
- Covers a larger area
- Protective cover
- Hot/cold therapy
- Quality materials
- Too large for some areas of the body
- Too large for microwave
To achieve a heat that is not excessive, you can heat the gel pack in the microwave for 1 or 2 minutes, but be aware that this may burn the synthetic material and cause skin burns. It can be used by men and women indistinctly, since it adapts easily to the anatomy of any person. It is recommended for arthritis and bruises.
- Material: Nylon
- Uses: Various body areas
- Type of adjustment: None
- Cover: Yes
- No. of units: 1 Gel Pack
- Hot/cold therapy
- Suitable for various body areas
- Not microwaveable
You will find great benefits in this pad, for example, the ease in achieving the desired therapeutic temperature. Just place in the microwave for a few seconds or chill in the refrigerator for at least two hours and that's it! Its design does not deform, which helps to a better adaptation in women and men, but too hot peel can cause skin burns.
- Heat/cold therapy
- Microwaveable
- Short therapy duration
Its design with soft seams helps maintain comfort during use and compresses sensitive areas through the gel pack. This generates the necessary support to transmit cold or heat effectively. Use the refrigerator and microwave to achieve the desired therapeutic temperature that relieves pain and deflates the ankle. It is important to consider that, in some users, the efficiency in maintaining the temperature was minimal.
- Material: Nylon
- Uses: Ankle and Foot
- Type of adjustment: Strap with Velcro
- Cover: Yes
- No. of units: 1
- Breathable materials
- 2 Protective sleeves
- Heat/cold therapy
- double adjustable strap with Velcro
- Not microwave safe
- Bulky design
This hot and cold thermal compression ankle brace will allow you to relieve the pain that prevents you from performing your daily activities and sports in a natural way. The size of its three gel cooling and warming sachets and its soft lining will prolong the wearing time, which will help you shorten the recovery period of an injury. In some cases of Achilles tendonitis, it may not provide the support needed to deflate the area.
Video: How to use hot and cold gel packs?
Types of hot & cold packs you should know about
What are the causes of muscle sprain?
As we mentioned earlier, these two entities are the most common musculoskeletal conditions:
Muscle contractures
A muscle contracture is nothing more than a permanent and involuntary contraction of the muscle. They are characterised by a shortening of the muscle fibres due to excessive strain. Every muscle must contract and expand in order to move properly. In contrast, when a muscle contracts, it does not relax and the area remains hardened and painful.
They occur depending on the timing of the physical exertion:
- During physical exertion: They usually occur when physical exertion is high, either due to a lack of training or due to the effort of the exercise. This is due to the body's inability to eliminate the products of muscle metabolism, resulting in pain and inflammation.
- After physical exertion: This is due to the inability of the muscle to return to its resting or relaxed state after physical exertion. After intense physical activity, a great deal of fatigue accumulates in it, which does not allow it to relax again.
- Residual contractures: These contractures occur after a muscle injury or trauma. As a defence mechanism, the muscle contracts to protect the injured area, but it tends to continue working even after the injury has healed. This persistence of the injury leads to residual muscle contracture.
We will now talk about the development and main causes of a muscle contracture:
- Overuse: This is one of the most common and highlighted causes. When sudden or continuous intensity is demanded of a muscle, it can become injured and contract. People who do not exercise frequently or do not prepare before exercising are more likely to suffer from muscle strains.
- Sudden temperature changes: When the muscle is subjected to a sudden change in temperature, it can cause an involuntary and painful contraction. It occurs much more often when the muscle is hot and exposed to extreme cold.
- Emotional stress: When an organism is exposed to a stressful situation, there is an accumulation of tension in all the muscles of the human body. This promotes the development of muscle contractures.
- Dehydration: The loss of water and electrolytes such as potassium, magnesium and glucose can lead to muscle failure. All of these elements allow the muscles to function properly, and when there is a deficit, normal metabolism is impaired, leading to contracture.
- Older age: Older people are more likely to suffer from muscle contractures because they lose elasticity and flexibility.
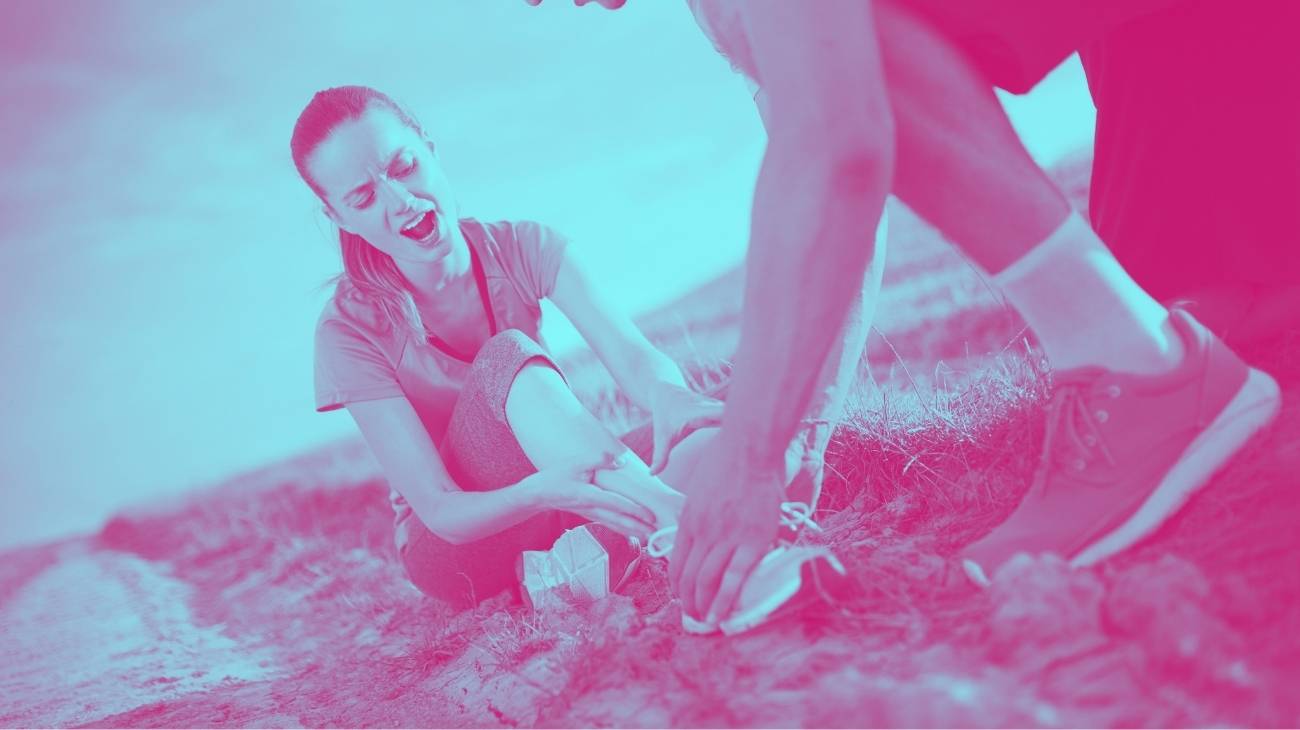
Sprains
Sprains are a completely different injury from muscle strains. While muscle strains occur in any muscle of the body, sprains are specifically limited to joints. Thus, sprains are defined as stretching, lengthening or tearing of the ligaments that connect joints. The most common sprain that people suffer is to the ankle.
Sprains are generally classified into three types depending on their severity:
- Grade I: This is the mildest form of sprain, where the ligaments are strained but not torn. With this grade, there is severe pain and even inflammation, but there is no restriction of movement.
- Grade II: This type of sprain is characterised by a partial tear of the ligament. In this case, the pain is much more intense and the joint is more restricted in its movement.
- Grade III: This is the most severe form, where there is a complete tear of the ligament, also with detachment of the bone. There may also be dislocation, which further compromises the integrity of the joint. In this case, there is immobility of the joint, extremely severe pain and surgical resolution.
The main reasons for sprains are:
- Sprain: Sprains are much more common on the lower limbs, especially the ankle. It occurs when the foot loses its stability while walking or running on an uneven surface.
- Certain sporting activities: Sharp twists or overloading a limb during sporting activities can cause sprains. They are common in knee, hand and thumb sprains.
- Trauma or fall: A blow to a limb can cause a sprain, as can a fall. Wrists are often injured by falls and handstands.
- Muscle fatigue: exhausted muscles are less able to support the joints well.
- Inadequate equipment: Sports equipment that is in poor condition can lead to injuries such as sprains. This is often the case with shoes that do not fit the foot because they are too big or too small.
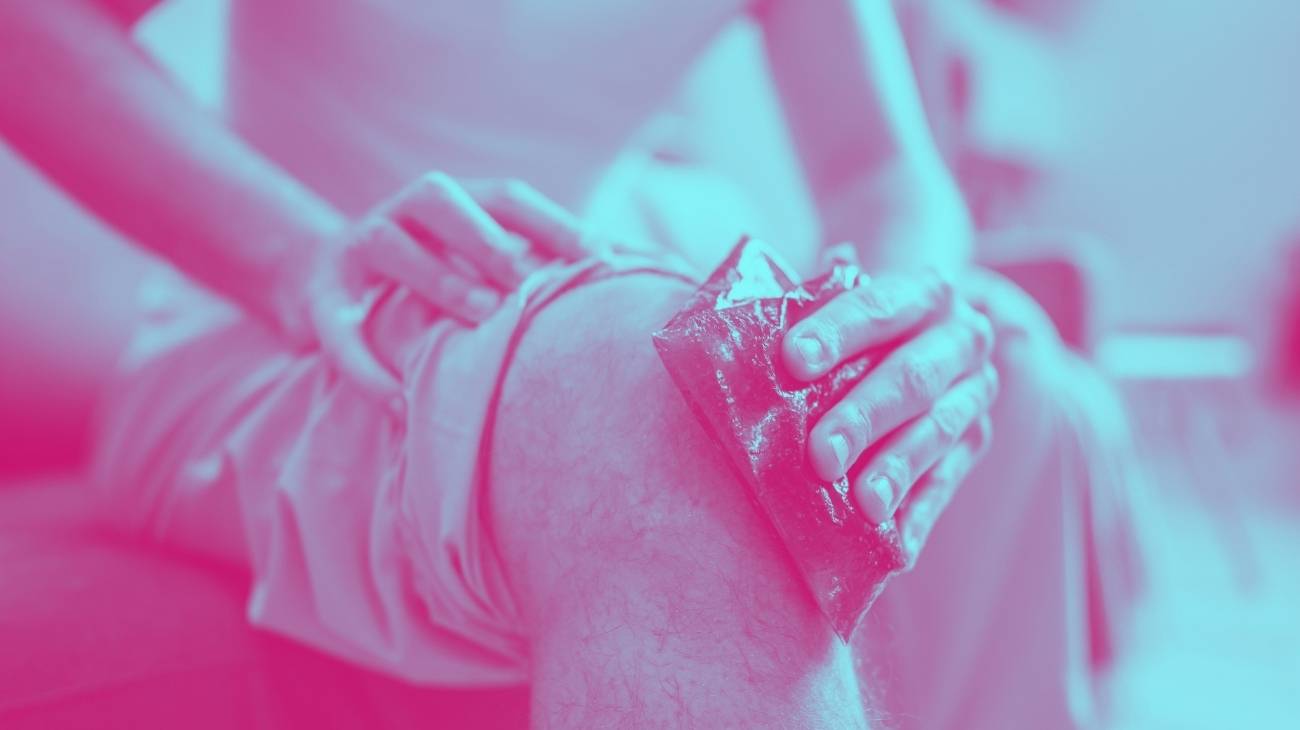
What is better for relieving muscle pain from sprains or strains: cold or heat?
Heat and cold therapies are one of the quickest and easiest ways to relieve the pain of muscle sprains or strains. Whether one or the other is used depends on whether the injury is acute or delayed. It is easiest to use hot or cold gel packs. It is important to know the benefits of each in order to prioritise their use:
Benefits of cold therapy
Cold therapy or cryotherapy is very helpful for inflammatory processes, especially when they are acute. Its effectiveness lies in its application within 48 to 72 hours after the muscle strain or sprain.
The inflammation is caused by dead and damaged cells, which trigger the invasion of repair cells, causing further inflammation. Cold also reduces the permeability of the capillaries, which prevents the extravasation of fluid into the interstitial tissue, thus preventing oedema.
The benefits of cold include:
- Reduced blood flow: Reduced blood flow due to vasoconstriction leads to less swelling and oedema.
- Disruption of pain transmission: Cold inactivates pain receptors in peripheral nerves, resulting in an analgesic response. Local application of cold causes itching for the first few seconds, then pain and finally pain relief.
- It promotes tissue regeneration: the resting phase allows the tissue to recover gradually and with a better response. The cold prevents haematomas and damage to the adjacent tissue, so that a significant improvement can be observed in a short time.
Benefits of heat therapy
Heat is also very effective in delaying musculoskeletal pain and inflammatory processes. Heat should never be applied to a wound that has just developed, as heat causes increased vasodilation. This leads to increased blood flow, which can aggravate an acute inflammatory process.
If an injury is more than 3-4 days old and pain persists, it will respond better to local heat. Vascular dilation allows for better blood flow, which allows more oxygen and nutrients to reach the damaged muscles and tissues. When the blood supply is better, repair cells can migrate and promote tissue healing.
When damaged ligaments and muscles improve significantly, pain is also greatly reduced. Some of the benefits of heat can be summarised as follows:
- It promotes healing and tissue regeneration: the increased blood flow allows better nutrition and oxygenation of the cells and tissues, which promotes muscle and ligament recovery.
- Increases elasticity and flexibility: the heat recovers the tissues and allows better relaxation of the ligaments and muscles, resulting in greater elasticity and flexibility.
- Reduces joint stiffness: This is due to its relaxing properties on ligaments and muscles.
- Pain relief: Heat also relieves pain by acting on the pain receptors of the peripheral nerves.
How do you use hot & cold gel packs to relieve sprains and muscle strains?
There are two ways to use them safely. They can be chilled in the freezer or refrigerator and heated in the microwave or in a water bath. The following explains how to use them properly at both temperatures:
Cold
Refrigerating the bags is very easy if you follow the recommendations below:
- Keep the gel pack in the refrigerator or freezer for at least 2 hours.
- Take the gel pack out of the freezer and check that it is at the correct temperature.
- Start applying to the wound area. With our packs, there is no need to place protective covers or cloths on the wound. They can be used directly as they have a soft binding on one side.
- Perform cold exposures for 10-15 minutes every hour. This should be repeated for 48 to 72 hours after the injury.
- Do not exceed the application time of the gel packs to avoid cold burns or skin damage.
- It is important to observe the site of the cold and watch for changes in skin colour.
- It is recommended to combine the therapy with periods of rest during which the affected area is elevated.
- Put the gel pack back in the freezer for later use.
Hot
If you have chosen to use the microwave, follow these recommendations for a safe process:
- Cook in the microwave at 800 W for 30 seconds.
- Check the heating process by monitoring the temperature by touch. The bag should be massaged so that the temperature is properly distributed in the pack.
- If the pouch is not at the right temperature, it can be heated for another 10 seconds.
- If the pouch gets too hot, leave it at room temperature and then heat it again.
- Once the temperature is perfect, you can start applying it to the area to be treated for 15 to 20 minutes every hour. This process can be repeated for as long as necessary.
- Check if the surface of the gel pack expands in the microwave. This just means that it has been overheated and you should let it cool down and then reheat it.
- If the bag breaks, let it cool and then discard it.
- Never heat a gel pack in the oven or on the grill.